ptmalloc2는 리눅스 GLIBC 에서 사용하는 메모리 할당자이다.
운영체제마다 메모리 할당자가 동작하는 방식은 각각 다르며, ptmalloc2는 리눅스 유저 모드에서 주로 사용하는 할당자다.
ptmalloc2는 glibc 2.23 버전, glibc 2.26(Tcache) 이후 버전 동작 방식이 조금 달라졌기 때문에 두 라이브러리 코드를 각각 비교하며 분석해야한다.
malloc_chunk
struct malloc_chunk {
INTERNAL_SIZE_T prev_size; /* Size of previous chunk (if free). */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T size; /* Size in bytes, including overhead. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk;
/* Only used for large blocks: pointer to next larger size. */
struct malloc_chunk* fd_nextsize; /* double links -- used only if free. */
struct malloc_chunk* bk_nextsize;
};ptmalloc2에서 힙 청크는 malloc_chunk 구조체를 사용하고 몇 가지의 멤버로 구성되어있다.
prev_size
- 이전 힙 청크가 해제되었을 경우 해제된 힙 청크의 크기를 저장한다.
- 해제되기 전까지는 이전 힙 청크의 데이터 영역으로 사용된다.
size
- 할당된 현재 힙 청크의 크기를 저장하고 있으며, 3개의 비트 플래그가 존재한다.
Flags (3bit)
- PREV_INUSE(P) : 해당 비트는 이전 힙 청크가 해제된 경우 설정 된다. 1은 이전 청크가 해제되지 않았을 경우, 0은 이전 청크가 해제된 경우 나타내는 값이다.
- IS_MMAPPED(M) : 해당 비트는 현재 청크가 mmap 시스템 콜을 사용하여 할당된 경우 설정된다.
- NON_MAIN_ARENA(N) : 해당 비트는 현재 청크가 main_arena에서 관리하지 않을 경우에 설정된다.
FD (ForwarD pointer)
- FD 포인터가 위치한 주소가 실제로 데이터 영역의 시작 부분이며, 할당되었을 때에는 사용하지 않는다.
- 힙 청크가 해제되었을 때 동일한 bin에 존재하는 다음 힙 청크를 저장한다.
BK (BacKward pointer)
- 동일한 bin 에서 이전 Free 청크의 포인터를 가리킨다.
fd_nextsize
- large_bin에서 사용하는 포인터로, 현재 힙 청크의 크기보다 작은 힙 청크의 주소를 가리킨다.
bk_nextsize
- large_bin에서 사용하는 포인터로, 현재 힙 청크의 크기보다 큰 힙 청크의 주소를 가리킨다.
동적으로 할당된 힙 메모리는 하나의 청크(Chunk) 라고 불리고, 청크는 malloc_chunk 구조체를 사용한다.
Allocate Chunk
- malloc이나 calloc 함수 등 동적 메모리 할당 함수를 통해 할당된 청크.
Free Chunk
- free 함수 등 동적 메모리 해제 함수를 통해 해제된 청크.
Top Chunk
- 힙 메모리의 마지막 위치해있는 청크를 말한다. Top Chunk의 마지막은 힙 메모리 영역의 끝이다.
- 메모리 할당 요청이 들어왔을 때, 사용할 적절한 Free Chunk가 없으면 Top Chunk를 쪼개어 사용한다.
Last Remainder Chunk
- 작은 사이즈의 할당 요청이 들어왔을 때, Free Chunk가 쪼개지고 남은 청크.
- Last Remainder Chunk는 연속된 작은 사이즈의 할당 요청이 들어왔을 때 비슷한 주소에 힙 청크가 할당되는 할당의 지역성을 유지시키기 위해 사용된다.
해제된 힙 청크(Free Chunk)는 bin 이라는 freelist 구조체를 통해 관리된다. freelist란 동적으로 메모리를 할당하고 해제할 때 메모리 관리의 효율을 높이기 위해 할당되지 않은 영역을 관리하는 연결 리스트이다. 영역을 해제할 때 해제하려는 영역을 freelist 추가하고, 할당 요청이 들어왔을 때 freelist에 추가된 영역을 제거하고 해당 영역을 사용한다.
ptmalloc2에서 사용하는 bin을 살펴보자
Fastbin
- 16 ~ 64 바이트 (32bit)
- 32 ~ 128 바이트 (64bit)
Unsortedbin
Smallbin
- 크기 < 512 바이트 (32bit)
- 크기 < 1024 바이트 (64bit)
Largebin
- 크기 >= 512 바이트 (32bit)
- 크기 >= 1024 바이트 (64bit)
malloc.c 내부의 주석
64 bins of size 8
32 bins of size 64
16 bins of size 512
8 bins of size 4096
4 bins of size 32768
2 bins of size 262144
1 bin of size what's left
main_arena
main_arena는 brk 시스템 콜을 사용하여 할당된 힙을 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 존재하는 malloc_state 구조체다.
main_arena에는 힙 청크를 관리하기 위한 배열과 포인터가 선언되어 있다.
top chunk의 크기보다 큰 사이즈의 할당 요청이 들어오면 mmap 시스템 콜을 사용하여 새로운 페이지를 할당한다. 이렇게 할당된 힙은 main_arena에서 관리하지 않는다.
main_arena
static struct malloc_state main_arena =
{
.mutex = _LIBC_LOCK_INITIALIZER,
.next = &main_arena,
.attached_threads = 1
};
malloc_state
struct malloc_state
{
/* Serialize access. */
__libc_lock_define (, mutex);
/* Flags (formerly in max_fast). */
int flags;
/* Fastbins */
mfastbinptr fastbinsY[NFASTBINS];
/* Base of the topmost chunk -- not otherwise kept in a bin */
mchunkptr top;
/* The remainder from the most recent split of a small request */
mchunkptr last_remainder;
/* Normal bins packed as described above */
mchunkptr bins[NBINS * 2 - 2];
/* Bitmap of bins */
unsigned int binmap[BINMAPSIZE];
/* Linked list */
struct malloc_state *next;
/* Linked list for free arenas. Access to this field is serialized
by free_list_lock in arena.c. */
struct malloc_state *next_free;
/* Number of threads attached to this arena. 0 if the arena is on
the free list. Access to this field is serialized by
free_list_lock in arena.c. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T attached_threads;
/* Memory allocated from the system in this arena. */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T system_mem;
INTERNAL_SIZE_T max_system_mem;
};
16 바이트와 32 바이트의 힙을 할당하고 해제하는 코드를 살펴보자.
/*
main_arena.c
gcc -o main_arena main_arena.c
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char *ptr = malloc(0x10);
free(ptr);
char *ptr2 = malloc(0x20);
free(ptr2);
}
위 코드를 실행하여 크기가 서로 다른 힙을 두 번 할당하고 해제한 모습이다.
fastbinY에 해제된 두 개의 힙 주소가 쓰여진 것을 확인할 수 있다.
fastbinY는 fastbin 크기로 할당되고 해제된 힙을 수용하기 위한 배열이다. 만약 해제된 힙과 동일한 크기를 할당하게 되면 fastbinY를 참조하여 할당할 것이다.
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char *ptr = malloc(32);
char *ptr2 = malloc(32);
char *ptr3 = malloc(32);
free(ptr);
free(ptr2);
free(ptr3);
return 0;
}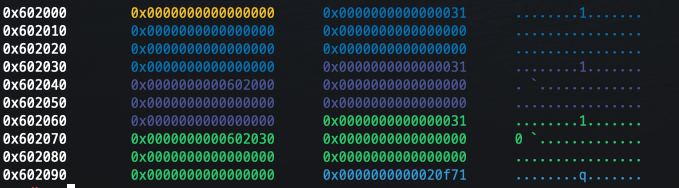
힙 청크가 해제되면서 FD에 포인터가 써진 것을 확인할 수 있다.

0x30 크기를 관리하는 두 번째 fastbin에 해제된 힙 청크의 주소가 단일 연결 리스트로 연결되어 있다.
이후에 같은 bin의 크기로 3개의 할당 요청이 들어온다면 0x602060, 0x602030, 0x602000 순서로 힙 청크가 재할당 될 것이다.
Fastbin
free (fastbin)
if ((unsigned long)(size) <= (unsigned long)(get_max_fast ()) // line 1
#if TRIM_FASTBINS
/*
If TRIM_FASTBINS set, don't place chunks
bordering top into fastbins
*/
&& (chunk_at_offset(p, size) != av->top)
#endif
) {
if (__builtin_expect (chunk_at_offset (p, size)->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ, 0)
|| __builtin_expect (chunksize (chunk_at_offset (p, size))
>= av->system_mem, 0))
{
/* We might not have a lock at this point and concurrent modifications
of system_mem might have let to a false positive. Redo the test
after getting the lock. */
if (have_lock
|| ({ assert (locked == 0);
mutex_lock(&av->mutex);
locked = 1;
chunk_at_offset (p, size)->size <= 2 * SIZE_SZ
|| chunksize (chunk_at_offset (p, size)) >= av->system_mem;
}))
{
errstr = "free(): invalid next size (fast)";
goto errout;
}
if (! have_lock)
{
(void)mutex_unlock(&av->mutex);
locked = 0;
}
}
free_perturb (chunk2mem(p), size - 2 * SIZE_SZ);
set_fastchunks(av);
unsigned int idx = fastbin_index(size);
fb = &fastbin (av, idx); // line 39
/* Atomically link P to its fastbin: P->FD = *FB; *FB = P; */
mchunkptr old = *fb, old2;
unsigned int old_idx = ~0u;
do
{
/* Check that the top of the bin is not the record we are going to add
(i.e., double free). */
if (__builtin_expect (old == p, 0))
{
errstr = "double free or corruption (fasttop)";
goto errout;
}
/* Check that size of fastbin chunk at the top is the same as
size of the chunk that we are adding. We can dereference OLD
only if we have the lock, otherwise it might have already been
deallocated. See use of OLD_IDX below for the actual check. */
if (have_lock && old != NULL)
old_idx = fastbin_index(chunksize(old));
p->fd = old2 = old; // line 58
}
while ((old = catomic_compare_and_exchange_val_rel (fb, p, old2)) != old2);
if (have_lock && old != NULL && __builtin_expect (old_idx != idx, 0))
{
errstr = "invalid fastbin entry (free)";
goto errout;
}
}fastbin은 작은 크기의 힙 청크를 할당하고 해제할 때 사용하는 bin이다.
fastbin은 다른 bin과는 달리 단일 연결 리스트를 사용하고 메모리 검증 루틴이 적기 때문에 ptmalloc2의 bin 중 할당 및 해제 속도가 가장 빠르다. 또한 할당 및 해제 시 LIFO(Last In First Out) 방식으로 청크를 처리하며, 다른 두 개의 청크가 인접해 있어도 하나의 청크로 병합되지 않는다.
위의 코드는 free 함수에서 fastbin 청크를 처리하는 코드이다.
청크가 해제될 때 해당 청크가 fastbin 크기의 범위에 속해 있다면 line 1의 조건문을 통과한다.
이후 line 39에서 현재 청크의 크기에 해당하는 fastbin의 리스트를 가져온다.
해당 fastbin freelist에 먼저 저장되어있는 청크가 존재하면, line 58에서 그 청크의 주소를 현재 해제된 청크의 FD에 저장한다. 이로 인해 해제된 청크가 fastbin의 단일 연결 리스트에 추가된다는 것을 알 수 있다.
Malloc (fastbin)
fastbin freelist에 들어있는 청크를 할당하는 과정이다.
if ((unsigned long) (nb) <= (unsigned long) (get_max_fast ()))
{
idx = fastbin_index (nb);
mfastbinptr *fb = &fastbin (av, idx); // line 4
mchunkptr pp = *fb;
do
{
victim = pp;
if (victim == NULL)
break;
}
while ((pp = catomic_compare_and_exchange_val_acq (fb, victim->fd, victim)) // line 12
!= victim);
if (victim != 0)
{
if (__builtin_expect (fastbin_index (chunksize (victim)) != idx, 0))
{
errstr = "malloc(): memory corruption (fast)";
errout:
malloc_printerr (check_action, errstr, chunk2mem (victim), av);
return NULL;
}
check_remalloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim); //return chunk ptr
alloc_perturb (p, bytes); //init
return p; // line 26
}
}
line 4에서 현재 요청된 fastbin 크기와 부합하는 fastbin의 인덱스를 찾는다.
line 12에서 선택된 청크의 FD를 참조하여 대상 청크의 FD가 가리키는 청크를 fastbin의 첫 번째 리스트로 업데이트하여 LIFO 구조를 유지한다.
최종적으로 마지막 라인에서 청크를 반환하면 해당 과정은 종료된다.
Unsorted bin (First In First Out)
unsorted bin은 small bin과 large bin 크기의 힙 청크가 해제되면 이후 재할당을 위해 사용되는 bin 이다.
bin의 개수는 1개이며, 해당 bin의 용도는 해제된 청크를 재사용하기 위해서 존재한다.
unsorted bin은 크기의 제한이 없기 때문에 다양한 크기의 힙 청크가 저장될 수 있다. 이는 이중 연결 리스트를 사용하며 해제된 청크를 재사용하기 위해서는 해제된 청크의 크기보다 작거나 동일한 크기의 청크가 할당되야 한다.
unsortedbin1
/* Take now instead of binning if exact fit */
INTERNAL_SIZE_T nb; /* normalized request size */
checked_request2size (bytes, nb);
size = chunksize (victim);
if (size == nb)
{
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size);
if (av != &main_arena)
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}unsortedbin1 은 unsorted bin의 size와 할당 요청이 들어온 크기인 nb를 비교한다. 이 두 개가 같은 크기라면 기존의 unsorted bin에 들어간 영역을 재사용한다.
unsortedbin2
if (in_smallbin_range (nb) &&
bck == unsorted_chunks (av) &&
victim == av->last_remainder &&
(unsigned long) (size) > (unsigned long) (nb + MINSIZE))
{
/* split and reattach remainder */
remainder_size = size - nb;
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
unsorted_chunks (av)->bk = unsorted_chunks (av)->fd = remainder;
av->last_remainder = remainder;
remainder->bk = remainder->fd = unsorted_chunks (av);
if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size))
{
remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL;
remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE | (av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot (remainder, remainder_size);
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}unsortedbin2는 할당 요청이 들어온 크기가 small bin 크기에 속하고, 현재 unsorted bin에 저장된 청크의 크기보다 작으며, unsorted bin에 존재하는 청크가 분할된 last_remainder 청크라면 이를 분할하여 남은 청크를 unsorted bin과 last_remainder에 저장한다.
unsortedbin3
if (in_smallbin_range (size))
{
victim_index = smallbin_index (size);
bck = bin_at (av, victim_index);
fwd = bck->fd;
}
victim->bk = bck;
victim->fd = fwd;
fwd->bk = victim;
bck->fd = victim;unsortedbin3은 다음 할당 요청까지 small bin의 크기가 unsorted bin에 남아있다면 해당 청크는 small bin으로 옮겨진다. 이는 크기를 검사하고 small bin 중 해당 크기에 적합한 배열을 찾아 small bin에 존재하는 청크와 FD, BK를 연결한다.
unsortedbin4
else
{
victim_index = largebin_index (size);
bck = bin_at (av, victim_index);
fwd = bck->fd;
if (fwd != bck)
{
/* Or with inuse bit to speed comparisons */
size |= PREV_INUSE;
/* if smaller than smallest, bypass loop below */
assert ((bck->bk->size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0);
if ((unsigned long) (size) < (unsigned long) (bck->bk->size))
{
fwd = bck;
bck = bck->bk;
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
else
{
assert ((fwd->size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0);
while ((unsigned long) size < fwd->size)
{
fwd = fwd->fd_nextsize;
assert ((fwd->size & NON_MAIN_ARENA) == 0);
}
if ((unsigned long) size == (unsigned long) fwd->size)
/* Always insert in the second position. */
fwd = fwd->fd;
else
{
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->bk_nextsize = victim;
victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim;
}
bck = fwd->bk;
}
}
else
victim->fd_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize = victim;
}
victim->bk = bck;
victim->fd = fwd;
fwd->bk = victim;
bck->fd = victim;unsortedbin4는 다음 할당 요청까지 large bin의 크기가 unsorted bin에 남아 있다면 해당 청크는 large bin으로 옮겨진다. 이는 크기를 검사하고 large bin 중 해당 크기에 적합한 배열을 찾아 large bin에 존재하는 청크과 fd_nextsize, bk_nextsize를 연결하고 FD, BK를 연결한다.
다음은 small bin 혹은 large bin 크기의 청크가 해제되면 unsorted bin에 삽입되는 과정이다.
else
clear_inuse_bit_at_offset(nextchunk, 0);
/*
Place the chunk in unsorted chunk list. Chunks are
not placed into regular bins until after they have
been given one chance to be used in malloc.
*/
bck = unsorted_chunks(av);
fwd = bck->fd;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck))
{
errstr = "free(): corrupted unsorted chunks";
goto errout;
}
p->fd = fwd; // line 17
p->bk = bck;
if (!in_smallbin_range(size)) // line 19
{
p->fd_nextsize = NULL;
p->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
bck->fd = p;
fwd->bk = p;
set_head(p, size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot(p, size);
check_free_chunk(av, p); // line 30
clear_inuse_bit_at_offset 매크로를 사용하여 인접한 다음 청크의 prev_inuse 비트를 0으로 만들고 line 17, 18에서 새롭게 해제된 청크를 이중 연결 리스트에 포함시킨다. (large bin은 FIFO 구조를 사용한다)
line 19에서 large bin범위에 속해있는 청크가 해제되었을 경우에는 unsorted bin에서 사용하지 않는 메타데이터인 fd_nextsize, bk_nextsize를 모두 NULL로 초기화 한다.
최종적으로 line 30에서 현재 청크가 해제되었는지 검증한다.
Small bin (First In First Out)
small bin은 512 바이트 미만의 사이즈로 청크가 해제 되었을 때 unsorted bin에 리스트가 추가된 후 저장되는 bin이다.
bin의 개수는 62개이며, 이중 연결 리스트를 사용한다. 해당 bin에는 두 개의 해제된 청크가 인접해 있을 수 없다. 만약 인접해 있다면 하나의 청크로 병합한다.
small bin 크기의 힙 청크가 해제되면 unsorted bin을 거쳐 small bin에 할당되게 된다.
if (in_smallbin_range (nb)) // line 1
{
idx = smallbin_index (nb); // line 3
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
if ((victim = last (bin)) != bin) // line 6
{
if (victim == 0) /* initialization check */
malloc_consolidate (av);
else // line 10
{
bck = victim->bk;
if (__glibc_unlikely (bck->fd != victim))
{
errstr = "malloc(): smallbin double linked list corrupted";
goto errout;
}
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, nb); // line 18
bin->bk = bck;
bck->fd = bin;
if (av != &main_arena)
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p; // line 27
}
}
}line 1에서 현재 요청된 크기가 small bin크기에 부합하는지 검사한 후, line 3에서 small bin에 해당되는 배열을 선정한다.
line 6에서 반한될 청크를 main_arena에서 얻어오면서 small bin의 연결 리스트가 비어있는지 확인한다. 만약 비어있다면 malloc_consolidate 함수를 호출하여 존재하는 fastbin과 병합하고 비어 있지 않다면 line 10에서 small bin인 힙 청크를 재할당하는 코드를 실행한다.
line 18에서 인접한 청크에 prev_inuse 비트를 설정하고 반환될 청크 뒤에 존재하는 청크를 main_arena가 BK로 가르키게 하고, 해당 청크의 FD는 main_arena를 가르키게 설정하여 이중 연결 리스트를 만들고 small bin의 첫 번째 리스트로 만든다.
최종적으로 청크를 반환하고 해당 과정을 종료한다.
Large bin (First In First Out)
large bin은 512 바이트 이상의 큰 크기의 청크가 해제 되었을 때 사용되는 bin 이다.
large bin의 개수는 63개이고, 이중 연결 리스트를 사영한다. large bin 청크의 구조체는 다른 bin과는 다르게 fd_nextsize, bk_nextsize를 사용한다. 이는 다른 크기의 large bin 청크들을 리스트로 연결하기 위해 사용된다.
if (!in_smallbin_range (nb)) // line 1
{
bin = bin_at (av, idx);
/* skip scan if empty or largest chunk is too small */
if ((victim = first (bin)) != bin && // line 6
(unsigned long) (victim->size) >= (unsigned long) (nb))
{
victim = victim->bk_nextsize;
while (((unsigned long) (size = chunksize (victim)) < // line 10
(unsigned long) (nb)))
victim = victim->bk_nextsize;
/* Avoid removing the first entry for a size so that the skip
list does not have to be rerouted. */
if (victim != last (bin) && victim->size == victim->fd->size)
victim = victim->fd;
remainder_size = size - nb;
unlink (av, victim, bck, fwd); // line 20
/* Exhaust */
if (remainder_size < MINSIZE)
{
set_inuse_bit_at_offset (victim, size);
if (av != &main_arena)
victim->size |= NON_MAIN_ARENA;
}
/* Split */
else // line 31
{
remainder = chunk_at_offset (victim, nb);
/* We cannot assume the unsorted list is empty and therefore
have to perform a complete insert here. */
bck = unsorted_chunks (av);
fwd = bck->fd;
if (__glibc_unlikely (fwd->bk != bck))
{
errstr = "malloc(): corrupted unsorted chunks";
goto errout;
}
remainder->bk = bck;
remainder->fd = fwd;
bck->fd = remainder;
fwd->bk = remainder;
if (!in_smallbin_range (remainder_size))
{
remainder->fd_nextsize = NULL;
remainder->bk_nextsize = NULL;
}
set_head (victim, nb | PREV_INUSE | // line 52
(av != &main_arena ? NON_MAIN_ARENA : 0));
set_head (remainder, remainder_size | PREV_INUSE);
set_foot (remainder, remainder_size);
}
check_malloced_chunk (av, victim, nb);
void *p = chunk2mem (victim);
alloc_perturb (p, bytes);
return p;
}
}line 1에서는 요청된 크기가 large bin 크기인지 검사한다.
그리고 line 6에서 large bin이 비어있는지, 혹은 가장 큰 청크가 요청된 크기보다 큰지 검사한다. 이후 line 10 victim->bk_nextsize를 순회하면서 요청된 크기에 부합하는 청크를 찾는다.
line 20에서는 반환될 청크를 제외한 앞 뒤 청크를 연결 리스트를 유지하기 위해 unlink 매크로를 사용한다.
line 30에서 large bin 청크가 요청된 크기보다 큰 경우 remainder_size를 검사하여 MINSIZE보다 크면 unsorted bin과 연결 리스트를 만들어 저장한다. 만약 last_remainder 청크의 크기가 large bin의 크기인 경우 쓰이지 않는 헤더인 fd_nextsize, bk_nextsize를 NULL로 초기화한다.
line 51에서 반환될 청크의 prev_inuse 비트를 설정한다. 또한 분활되어 남은 청크인 last_remainder 청크 또한 prev_inuse비트를 설정해 현재 반환될 청크가 할당된 상태임을 나타낸다.
'Pwnable > Techniques' 카테고리의 다른 글
| _int_free (0) | 2021.02.22 |
|---|---|
| _int_malloc (0) | 2021.02.22 |
| _IO_FILE vtable check (0) | 2021.02.06 |
| _IO_FILE (0) | 2021.02.03 |
| seccomp (0) | 2021.02.02 |




댓글